If you do not use the accrual principle, then you are using the cash method of accounting, where you record revenue when cash is received and expenses when they are paid. There are also modified versions of the cash method of accounting that allow for the limited use of accruals. You must report the $1,000 on your 2017 income tax return, the year the $1,000 was earned. When using the accrual method, income is recognized when it is earned. What this means is that all of the circumstances that are required for a person to complete a job for income must be met for recognition.
With the accrual method, you record expenses as they are incurred, not when you exchange cash. The cash-basis method of accounting does not cash basis vs accrual basis accounting recognize accrued liabilities. Similarly, a salesperson, who sold the product, earned a commission at the moment of sale (or delivery).
Cash Basis Systems Lack Built-in Error Checking
The way a company records payment of payroll taxes, for example, differs with these two methods. The entry goes into a tax liability account (an account for tracking tax payments that have been made or must still be made). If the company incurs $1,000 of tax liabilities in March, that amount is entered in the tax liability account even if it hasn’t yet paid out the cash. As a result, it is challenging to build a single-entry system that conforms to the GAAP requirements for businesses in most countries (Generally accepted accounting principles).
Can you mix cash and accrual accounting?
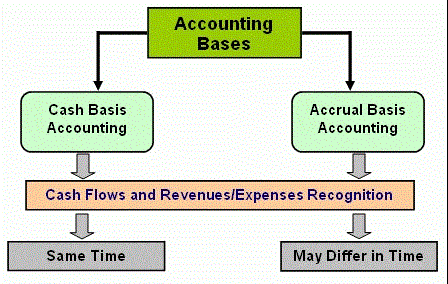
The accrual basis of accounting. For example, a company operating under the accrual basis of accounting will record a sale as soon as it issues an invoice to a customer, while a cash basis company would instead wait to be paid before it records the sale.
Cash Basis Accounting (Cash Accounting)
Usage Explained With Examples, Contrast with Accrual Accounting
Deciding between cash basis or accrual basis accounting really depends on the state of your business. For reporting http://textbooksproject.org/?p=40679 purposes, accrual basis will usually provide better financial intelligence on the true state of your business.
Cash Basis Accounting is Simple and May be Sufficient for Some Small Businesses.
An example of accrual basis accounting is to record revenue as soon as the related invoice is issued to the customer. The upside is that the accrual basis gives a more realistic idea of income and expenses during a period of time, therefore providing a long-term picture of the business that cash accounting can’t provide.
Accrued expense
With the accrual method, income and expenses are recorded as they occur, regardless of whether or not cash has actually changed hands. The sale is entered into the books when the invoice is generated rather than when the cash is collected. Likewise, an expense occurs when materials are ordered or when a workday has been logged in by an employee, not when the check is actually written. The downside of this method is that you pay income taxes on revenue before you’ve actually received it. The accrual basis of accounting is a system of accounting in which the adjustments are needed to assign revenues to periods in which they are earned and to match expenses with revenues.
The company will recognize the commission as an expense in its current income statement, even though the salesperson will actually get paid at the end of the following week in the next accounting period. The commission is also an accrued liability on the balance sheet for the delivery period, but not for the next period when the commission (cash) is paid out to the salesperson. A key advantage of the accrual basis is that it matches revenues with related expenses, so that the complete impact of a business transaction can be seen within a single reporting period. Using cash basis accounting, income is recorded when you receive it, whereas with the accrual method, income is recorded when you earn it. Now imagine that the above example took place between November and December of 2017.

- Accrual accounting is an accounting method that measures the performance of a company by recognizing economic events regardless of when the cash transaction occurs.
- You select an accounting method by placing a check mark in the box that applies to you when you file Schedule C.
- That way, recording income can be put off until the next tax year, while expenses are counted right away.
Expenses are recorded in the books and reported on your tax return in the year paid. The accrual basis of accounting is the concept of recording revenues when earned and expenses as incurred. The use of this approach also impacts the balance sheet, where receivables or payables may be recorded even in the absence of an associated cash receipt or cash payment, respectively.
Under accrual accounting, therefore, both sellers and buyers report revenues and expenses based on each party’s first pair of entries. They state, that is, entries showing income earned by the seller and cash owed by the buyer.
Deciding between cash basis accounting and accrual basis accounting can be a difficult decision when you are first starting your business. Each offers different viewpoints into your company’s financial wellbeing.
Who must use accrual method of accounting?
The accrual method is required if the entity fails both the $1 million and the material income-producing factor tests. The accrual method is required if the company has more than $5 million in average sales. The exhibit below includes a flow chart to help small businesses select the proper accounting method.
Accrual basis is a method of recording accounting transactions for revenue when earned and expenses when incurred. The accrual basis requires the use of allowances for sales returns, bad debts, and inventory obsolescence, which are in advance of such items actually occurring.
One of the differences between cash and accrual accounting is that they affect which tax year income and expenses are recorded in. This in turn produces financial statements that are comparable over time. Accrual accounting is an accounting What is bookkeeping method whereby revenue and expenses are recorded in the periods in which they are incurred. If the same carpenter uses accrual accounting, his bottom line is different. In this case, he books his expenses when they’re actually incurred.
This lack may not concern sole proprietorships, partnerships, or small privately held companies. For these firms, the what is accrual accounting accounting system must support only the company’s needs to comply with tax and employment reporting requirements.
Companies using cash basis accounting record revenues when they receive cash and expenses when they pay cash. Cash accounting is a bookkeeping method in which revenues and expenses are recorded when received and paid, respectively, not when incurred. GrowthForce provides detailed reporting for your business backed by bookkeeping and accounting you can trust. We have clients who use both cash basis and accrual basis accounting and can provide reports needed to drive profitability for your company.
The cash basis of accounting recognizes revenues when cash is received, and expenses when they are paid. This method does not recognize accounts receivable or accounts payable. The difference between cash and accrual accounting lies in the timing statement of retained earnings example of when sales and purchases are recorded in your accounts. Cash accounting recognizes revenue and expenses only when money changes hands, but accrual accounting recognizes revenue when it’s earned, and expenses when they’re billed (but not paid).

What is Accrual Accounting?
So for example, if you agree to paint a house for $1,000 and receive half prior to beginning the job you would not recognize that first $500 as income at first. When the job is completed, you recognize the entirety of the $1,000 regardless of whether you have received the other half of the payment yet. The expenses associated with the job are recognized at the same time as the associated income. So, in the house example, if you spent $200 for paint, the expense is realized when the job is completed along with the $1,000 fee. The accrual basis of accounting is advocated under both generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and international financial reporting standards (IFRS).